Write a message
Email Address
support@advering.com
An application is any program, or group of programs, that is designed for the end user. Applications software (also called end-user programs) include such things as database programs, word processors, Web browsers and spreadsheets.
Maybe you’ve sat down with your employees and tried to nail down the best way to encourage more of this wallet-opening engagement from your customers. You want to increase their interaction with your business to promote sales, of course, but you also want to provide a level of value for your customers that they can’t get anywhere else.
One way to do this is create a loyalty program within your app. It would work like this:
The more customers interact with your business and product, the more points they collect, which can in turn be used for great deals on the products they already know they want.
Starbucks uses their mobile app to their advantage by offering rewards exclusively to app subscribers, which then motivates customers to buy coffee (And other delicious snacks) from them. They’re even more ahead of the curve by allowing their users to pay directly from the app, speeding up the whole transaction process.
when your customers see their points adding up in real time (rather than having to send in points in the mail or wait until they can access your website to enter them manually), they’ll be impressed and more enticed to follow up on their purchases in the future.

Questions to Ask Yourself:
Mobile event apps come in three basic forms: native apps, web-based apps, and hybrid apps. Each of these types of apps has its own unique advantages, and depending on your specific needs, one option might be better suited for your event than the others.
The decision to build either a native, web, or hybrid mobile app should be based on your business objectives. Before jumping into development, you should consider the following factors:
Whichever approach you choose should, above all, be quick, responsive, and reliable. As users are demanding more from mobile experiences, it’s important to keep up with their changing demands. Whichever app you decide to build, remember the following:
Finally, it’s important to work with an app development company that specializes in platform specific design and development.
Source
Developing an application can be a daunting task, but launching it shouldn’t be. There’s no simple answer to the question of which one should you develop for first, Android or Apple. It depends on various number of factors and circumstances which may influence the final decision. Even if your budget allows you to build a native application for every existing platform, various factors should be considered beforehand.
This is the best way you can judge their experience and expertise. A thorough walkthrough of their portfolio will be the most rational step (at first place) to know their quality of work and the clients they have worked for. You will also get a list of their repeat clients and authentic facts and figures. Ask them to provide pioneering projects (if any) from their portfolio.
Ask them to provide real-time app links on Google Play, App Store, Microsoft Store. You must download and use that app to test not just how it looks (UI) but how it interacts with the user (UX). Don’t forget, user experience matters the most.
Don’t be in a hurry to select any app developer and app development company. It’s important to pick a service provider carefully so that the final, end product (a mobile app in this case) matches your requirements and works exactly how you always wanted.
Source
The first and, potentially, most important part of creating an app. Think about it, what is the point of creating every detail of a project only to find out someone else is already doing the exact same thing in the exact same way; remember great minds think alike and you’re not the only one in this world.
Start with the question, “What is it that makes my app different?” This can be a thing of values, a unique algorithm, unique logo, anything really that can distinguish yourself from competition. Some people have had success in their marketing ability alone.
Do a simple search on some of the keywords your app might be listed on Google or within the app stores (i.e. Denver mobile apps or Denver seo for us, depending on the project that you are creating <your location> + <your project>). Check out the competition, if any, to see who you are up against. The more time your spend on research the more you will know your purpose, direction, and goal for your application.
I can say without a reasonable doubt that as a human being that is alive in 2017, you have interacted with many different types of apps. Have you ever noticed that depending on what application you use the orientation changes? Some jump straight into a landscape view and others stay in a portrait view. Why do you think this might be? Again, we’re confronted with nihilistic question, “What does it all matter!!!???” Your device orientation can completely, once again, change the interaction a user has with your app (notice how that idea keeps coming up, curious huh?). What if you had four drop down boxes that you wanted to sit side by side from left to right. Imagine what it would look like when in a portrait view, potentially, crunching all the text to the point that makes it hard to read what you’re selecting. How might this affect the popularity of your app if it’s not built with a responsive design that makes it easier for users to interact with.
When looking beyond Google Play, the Amazon App Store is the place to start. Here you can get thousands of free and paid apps, as well as paid apps for free.
Amazon gives away a paid app for free every day and using Amazon's dedicated app store is the only way to access them. Amazon also regularly offers free bundles of paid apps (good ones, too).
Aside from great free titles, the Amazon App Store has a huge selection books, movies and songs – often at lower prices than on Google Play. Download the Amazon app at the link, but be aware that you must have an Amazon account to use the service.
F-Droid can be installed from the official website, and it certainly presents refreshing idea. Unlike other app stores, F-Droid is funded by donations, and the apps themselves don’t have reviews or ratings. But all of the apps contained within there are FOSS (Free and Open Source Software).
It's an excellent app store for developers because anyone can access the code of these apps for free. You might find a particular app feature or functionality which you like and would want to use for your own app, and you can, just access the code and copy it.
The downside is that the apps are not always as "professional" as can be found in stores like Google Play and the Amazon app store. Still, for developers, it's highly recommended.
We want you to find the greatest apps available in the App Store and other markets. In the easiest, cheapest and most entertaining way. Enjoy.
App 704
Drag, drop and create hybrid apps for Android, iOS, BlackBerry, Windows, and Kindle with a simple and quick cloud app builder. AppyPie is the fastest growing free iPhone app maker out there. There is nothing to download and install, everything gets done in a well-structured interface. Since its launch in 2013, the service has been growing rapidly, attracting users from all over the world with its simplicity, modernity and variety of features. This Indian platform remains faithful to its idea – creating an app with it is as easy as pie.
The following features of AppyPie help it win the affection of users:
The not-so-pleasant sides of AppyPie free version are:
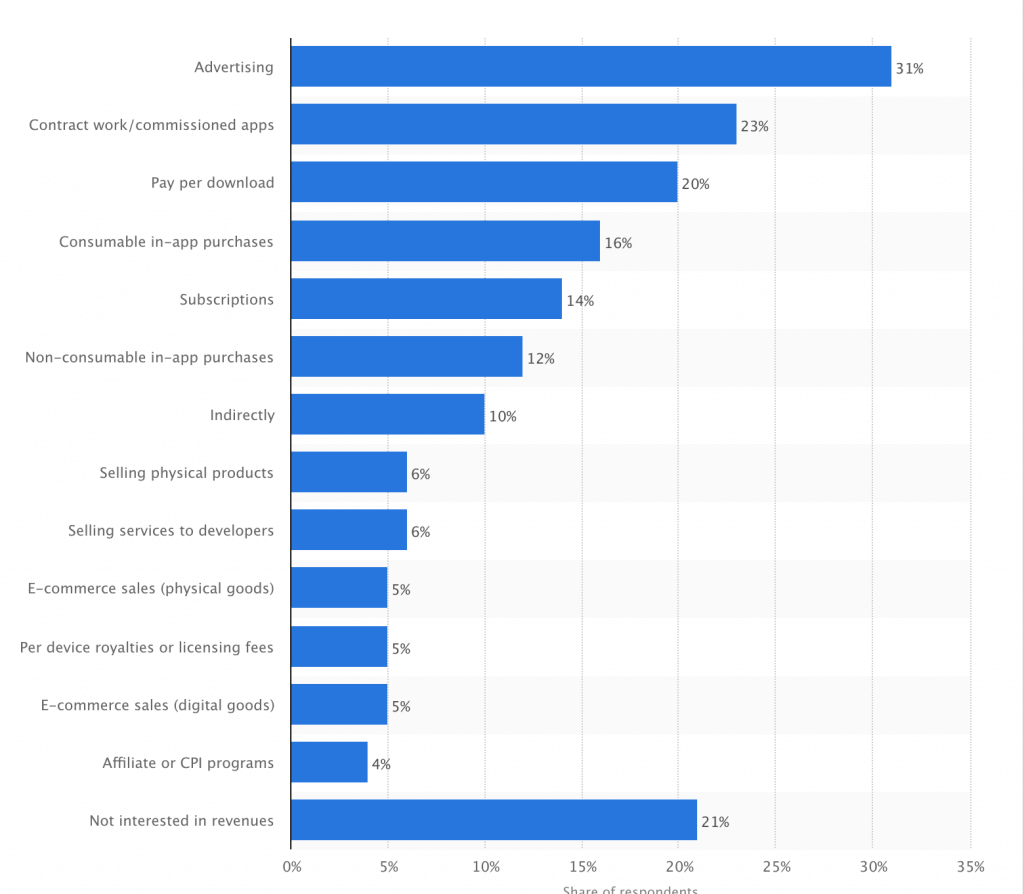
Advertising is probably the most common and easiest to implement, and it is done via a third-party ad network.
7 out of 10 free apps providers used advertising as their revenue model in 2016.
Using ads to monetize an app and make money is quite simple. An app owner just needs to display commercials inside their mobile app and get paid from the third-party ad networks.
You can get paid every time an ad is displayed (per impression), per click on the ad, and when a user installs the advertised app.
There are mainly 4 types of ads that are displayed by the app providers for monetization.